Home Equity Loan Rates: Everything You Need To Know
Starting with home equity loan rates, understanding how they work and what factors influence them is crucial for homeowners looking to leverage their home’s equity.
Exploring the various types of home equity loans, current trends in rates, and how they compare to mortgage rates can help borrowers make informed decisions about their financial future.
Overview of Home Equity Loan Rates
Home equity loan rates refer to the interest rates charged on loans that are secured by the borrower’s home equity. These rates are typically lower than other types of loans because the home acts as collateral, reducing the risk for lenders.
Factors that influence home equity loan rates include the borrower’s credit score, the amount of equity in the home, the loan-to-value ratio, and current market conditions. A higher credit score and more home equity generally result in lower interest rates, while a higher loan-to-value ratio may lead to higher rates.
To calculate home equity loan rates, lenders typically start with a base rate, such as the prime rate, and then add a margin based on the borrower’s credit profile and loan terms. For example, if the prime rate is 3.25% and the lender’s margin is 2%, the total interest rate would be 5.25%.
Example of Home Equity Loan Rate Calculation
- Lender’s Base Rate: Prime Rate (3.25%)
- Lender’s Margin: 2%
- Total Interest Rate: 5.25%
Types of Home Equity Loans
When considering a home equity loan, it’s important to understand the different types available and how they can impact your financial situation. Let’s explore the various options to help you make an informed decision.
Cash-Out Refinance
Cash-out refinance allows you to replace your current mortgage with a new one for more than you owe, receiving the difference in cash. This type of loan typically offers lower interest rates than other forms of borrowing.
Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC)
HELOC functions as a revolving line of credit, allowing you to borrow against the equity in your home as needed. Interest rates are typically variable, meaning they can fluctuate over time.
Home Equity Loan
A home equity loan provides a lump sum of money upfront, with a fixed interest rate and predictable monthly payments. This option may be suitable for those who prefer stability in their borrowing costs.
| Feature | Fixed-Rate Home Equity Loan | Adjustable-Rate Home Equity Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Fixed for the term of the loan | Can fluctuate based on market conditions |
| Payment Structure | Consistent monthly payments | Potentially changing payments |
| Flexibility | Less flexibility in adjusting payments | May offer lower initial rates |
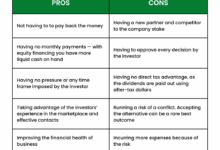
Each type of home equity loan has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. While a cash-out refinance may be beneficial for those looking to secure a lower interest rate, a HELOC could be more suitable for individuals who anticipate varying borrowing needs. On the other hand, a home equity loan with a fixed rate could offer peace of mind for those seeking predictability in their monthly payments. Choose the option that aligns best with your financial goals and needs.
Current Trends in Home Equity Loan Rates
When looking at the current trends in home equity loan rates, it’s important to compare rates offered by different financial institutions and understand the factors that influence these rates.
Comparison of Home Equity Loan Rates
Let’s take a look at the current home equity loan rates offered by three different financial institutions:
- Bank A: 3.5%
- Credit Union B: 4.0%
- Online Lender C: 4.5%
Factors Influencing Fluctuations in Rates
Several factors contribute to fluctuations in home equity loan rates, including market conditions, lender policies, and borrower creditworthiness. Lenders may adjust rates based on changes in the economy or their own financial stability, impacting the rates offered to borrowers.
Historical Changes in Home Equity Loan Rates
To visualize the historical changes in home equity loan rates over the past five years, a line graph can be created to show the fluctuations in rates over time. This graph can help illustrate how rates have evolved and provide insight into potential future trends.
Impact of Federal Reserve’s Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy plays a significant role in influencing home equity loan rates. Changes in the Fed’s interest rates can impact borrowing costs for homeowners, as lenders may adjust their rates in response to these changes. Understanding the Fed’s policy decisions can help borrowers anticipate potential changes in loan rates.
Evaluation of Fixed-Rate vs. Variable-Rate Loans
When considering fixed-rate versus variable-rate home equity loans, it’s essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each option. Fixed-rate loans offer stability in payments, while variable-rate loans may provide flexibility but can also be subject to interest rate changes. Borrowers should assess their financial situation and risk tolerance to determine the most suitable loan type for their needs.
Shopping for the Best Home Equity Loan Rates
When looking for the best home equity loan rates, it’s essential to consider various factors that can influence the overall cost of the loan. Factors such as credit score, loan-to-value ratio, and fees can all impact the interest rates offered by lenders. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
Factors Influencing Home Equity Loan Rates
- Credit Score: A higher credit score typically leads to lower interest rates as it indicates lower risk for the lender.
- Loan-to-Value Ratio: Lenders may offer better rates for borrowers with lower loan-to-value ratios, which is the percentage of your home’s value that you are borrowing against.
Calculating the Total Cost of a Home Equity Loan
When calculating the total cost of a home equity loan, consider not only the interest rates but also fees and other charges involved. Use this formula:
Total Cost = Loan Amount + Interest + Fees + Other Charges
Reputable Lenders with Competitive Rates
Some reputable lenders known for competitive home equity loan rates include [Lender 1], [Lender 2], and [Lender 3]. It’s always advisable to compare offers from multiple lenders to find the best rate.
Risks of Selecting a Loan Based Solely on Low Interest Rates
- Hidden Fees: Some lenders may compensate for low interest rates by charging higher fees, increasing the overall cost of the loan.
- Variable Rates: Opting for a loan with variable rates can lead to fluctuations in monthly payments, impacting your financial stability.
Comparison Table for Loan Offers
| Lender | Interest Rate | Fees |
|---|---|---|
| [Lender 1] | [Interest Rate 1] | [Fees 1] |
| [Lender 2] | [Interest Rate 2] | [Fees 2] |
Leveraging Pre-Approval Offers for Negotiation
Use pre-approval offers from one lender to negotiate better terms and rates with others. This can help you secure a more favorable deal based on competing offers.
Monitoring Fluctuations in Home Equity Loan Rates
Utilize resources like financial websites or tools that track home equity loan rates to stay informed about market trends. This can help you make decisions at the right time to secure the best rates available.
Home Equity Loan Rates vs. Mortgage Rates
When considering borrowing against the equity in your home, it’s essential to understand the differences between home equity loan rates and mortgage rates. While both types of loans are secured by your property, they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics.
Home equity loan rates are typically higher than mortgage rates because they are considered riskier for lenders. This is because home equity loans are secondary to the primary mortgage, meaning that in the event of default, the primary mortgage lender gets paid first. As a result, home equity loan rates are influenced by factors such as the borrower’s credit score, loan-to-value ratio, and the amount of equity in the home.
On the other hand, mortgage rates are generally lower than home equity loan rates because the primary mortgage is the first lien on the property. Mortgage rates are influenced by broader economic factors such as inflation, the overall state of the economy, and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy.
Differences in Factors Influencing Rates
- Home Equity Loan Rates:
- Dependent on borrower’s credit score.
- Affected by loan-to-value ratio.
- Influenced by the amount of equity in the home.
- Mortgage Rates:
- Impacted by broader economic factors.
- Influenced by inflation rates.
- Tied to the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy.
Scenarios for Choosing Between Home Equity Loan and Mortgage
- If you need a large sum of money upfront for a specific purpose like home renovations, a home equity loan may be more beneficial due to potentially lower closing costs compared to refinancing your mortgage.
- On the other hand, if you are looking for a lower overall interest rate and a longer repayment term, refinancing your mortgage at a lower rate might be the better option.
Risks Associated with Fluctuating Home Equity Loan Rates
Fluctuating home equity loan rates can pose several risks to borrowers, impacting their monthly payments and overall financial stability. It is essential for borrowers to understand these risks and be prepared to mitigate them effectively.
Interest Rate Risk
One of the primary risks associated with fluctuating home equity loan rates is interest rate risk. As interest rates rise, borrowers with variable-rate home equity loans may see an increase in their monthly payments, potentially creating financial strain. To mitigate this risk, borrowers can consider refinancing to a fixed-rate loan or setting aside funds to cover potential payment increases.
Payment Shock
Another risk is payment shock, where borrowers may experience a significant increase in their monthly payments due to rising interest rates. This sudden change can disrupt their budget and financial planning. To avoid payment shock, borrowers should carefully assess their ability to handle potential payment increases before taking out a home equity loan.
Equity Erosion
Fluctuating home equity loan rates can also impact the equity in a borrower’s home. If property values decrease or if borrowers take out additional loans against their home, they may find themselves owing more than the home is worth. This can lead to challenges in selling the home or refinancing in the future. Borrowers can protect their equity by making timely payments and avoiding excessive borrowing against their home.
Factors That Impact Home Equity Loan Rates
When it comes to home equity loan rates, there are several key factors that can influence the interest rate you receive. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions when shopping for a home equity loan.
Credit Scores
Your credit score plays a significant role in determining the interest rate you will be offered on a home equity loan. Lenders use your credit score to assess your creditworthiness and the likelihood that you will repay the loan on time. Generally, the higher your credit score, the lower the interest rate you will qualify for. A good credit score can result in substantial savings over the life of the loan in the form of lower interest payments.
Loan-to-Value Ratios
Another important factor that impacts home equity loan rates is the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. This ratio is calculated by dividing the amount of the loan by the appraised value of your home. The higher the LTV ratio, the riskier the loan is for the lender. As a result, borrowers with lower LTV ratios typically receive lower interest rates. Lenders often offer more competitive rates to borrowers who have a significant amount of equity in their homes, as they pose less risk of default.
Calculating Home Equity Loan Rates
When it comes to understanding home equity loan rates, it’s essential to know how these rates are calculated. By knowing the formula and factors involved, you can make informed decisions when choosing a home equity loan.
To calculate home equity loan rates, the following formula is typically used:
Home Equity Loan Rate = Prime Rate + (Lender’s Margin)
The Prime Rate is a benchmark interest rate used by financial institutions, while the Lender’s Margin is the additional percentage that the lender adds to the Prime Rate to determine the final rate for the borrower.
Examples of Calculations for Different Loan Scenarios
To better understand how this formula works, let’s consider two different loan scenarios:
1. Prime Rate = 3.25%, Lender’s Margin = 2%
Home Equity Loan Rate = 3.25% + 2% = 5.25%
2. Prime Rate = 4%, Lender’s Margin = 1.5%
Home Equity Loan Rate = 4% + 1.5% = 5.5%
These examples show how varying Prime Rates and Lender’s Margins can impact the final home equity loan rate for borrowers.
Comparing Interest Rates from Different Financial Institutions
| Financial Institution | Prime Rate | Lender’s Margin | Home Equity Loan Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank A | 3.5% | 2.5% | 6% |
| Credit Union B | 3.75% | 2% | 5.75% |
This table provides a comparison of home equity loan rates from different financial institutions, showcasing the importance of shopping around for the best rates.
The key factors that influence home equity loan rates include the borrower’s credit score, loan amount, loan-to-value ratio, and the overall economic climate. By understanding these factors and the calculation formula, borrowers can make informed decisions when selecting a home equity loan.
Benefits of Home Equity Loan Rates
Securing a home equity loan with favorable rates can offer numerous benefits to borrowers, providing them with opportunities to achieve their financial goals and save money in the long run.
Financial Flexibility
- Home equity loan rates allow borrowers to access a large sum of money upfront, which can be used for various purposes such as home renovations, debt consolidation, or emergency expenses.
- Lower interest rates on home equity loans compared to other types of loans make them an attractive option for borrowers looking to manage their finances efficiently.
Savings on Interest Payments
- By securing a home equity loan with low rates, borrowers can save significant amounts of money over the life of the loan, reducing the overall cost of borrowing.
- For example, a borrower with a $50,000 home equity loan at a 5% interest rate would pay $10,000 in interest over five years, compared to $15,000 at a 10% interest rate, resulting in $5,000 in savings.
Qualifying for Competitive Home Equity Loan Rates
When it comes to securing competitive home equity loan rates, there are certain requirements and factors that play a crucial role in determining your eligibility. Lenders consider various aspects of your financial profile to offer you the best rates possible.
Factors Affecting Eligibility for Lower Home Equity Loan Rates
- Good Credit Score: A higher credit score demonstrates your creditworthiness and can help you qualify for lower rates.
- Stable Income: Lenders prefer borrowers with a stable income as it indicates the ability to repay the loan on time.
- Low Debt-to-Income Ratio: A lower ratio signifies that you have enough income to cover your debts, making you less risky to lenders.
- Equity in Your Home: The more equity you have in your home, the better your chances of qualifying for competitive rates.
Tips to Improve Eligibility for Lower Home Equity Loan Rates
- Monitor and Improve Your Credit Score: Pay your bills on time, keep credit card balances low, and avoid opening new credit accounts before applying for a home equity loan.
- Reduce Your Debt: Pay down existing debts to lower your debt-to-income ratio and increase your chances of qualifying for better rates.
- Shop Around: Compare offers from different lenders to find the best rates and terms that suit your financial situation.
Role of Income, Credit History, and Other Factors
- Income Stability: Lenders assess your income stability to ensure you can meet the loan obligations without financial strain.
- Credit History: Your credit history reflects your past borrowing behavior and plays a significant role in determining the interest rates offered to you.
- Loan-to-Value Ratio: The loan-to-value ratio, which compares the amount of the loan to the appraised value of the property, also influences the rates you qualify for.
Home Equity Loan Rates and Tax Implications
When it comes to home equity loan rates, understanding the tax implications is crucial for borrowers. Changes in rates can impact tax deductions and overall financial planning. Let’s delve into how home equity loan rates affect taxes and what borrowers need to consider.
Tax Deductions and Home Equity Loan Rates
- Home equity loan interest payments are tax-deductible for loans up to $100,000 if the funds are used for home improvements.
- Fluctuations in home equity loan rates can affect the amount of interest paid and, consequently, the tax deductions available.
- Higher rates mean higher interest payments, leading to increased tax deductions for eligible expenses.
Differences in Tax Treatment: Fixed vs. Variable Rates
- Fixed-rate home equity loans offer stable monthly payments and interest rates, making it easier to predict tax deductions.
- Variable-rate home equity loans can lead to fluctuating interest payments, impacting tax deductions based on the current rate environment.
- Borrowers need to stay informed about changes in rates to adjust their tax planning accordingly.
Maximizing Tax Deductions with Home Equity Loan Interest Payments
- By strategically using home equity loan funds for eligible expenses, borrowers can maximize tax deductions on interest payments.
- Planning ahead and keeping track of expenses can help optimize tax benefits while managing home equity loan rates effectively.
Impact of Interest Rate Changes on Tax Benefits
- Changes in interest rates can influence the overall tax benefits derived from a home equity loan.
- Lower rates may result in reduced interest payments and lower tax deductions, while higher rates can lead to increased deductions.
- Borrowers should assess the tax implications of rate changes and adjust their financial strategies accordingly.
Understanding APR vs. Interest Rates for Home Equity Loans
When considering a home equity loan, it’s essential to understand the difference between APR (Annual Percentage Rate) and interest rates. While interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money, APR includes additional fees and charges, providing a more comprehensive view of the total cost of the loan.
Relationship between APR and Interest Rates
APR is calculated by taking into account the interest rate, lender fees, closing costs, and other charges associated with the loan. This means that APR is typically higher than the interest rate alone, as it encompasses all the expenses incurred when taking out the loan.
Impact of APR on Home Equity Loan Cost
A higher APR can significantly increase the overall cost of a home equity loan. Borrowers should pay attention to the APR when comparing loan offers, as a lower APR can result in substantial savings over the life of the loan.
Examples of APR vs. Interest Rates
For example, a home equity loan with a 5% interest rate and 1% in fees would have an APR of 6%. This means that the borrower would pay 6% annually on the total loan amount, including fees.
Effects of Varying APR Rates on Monthly Payments
Higher APR rates lead to higher monthly payments on a home equity loan. A small difference in APR can result in a significant increase in monthly payments over time, impacting the borrower’s budget.
Breakdown of Fees Included in APR
| Fee Type | Amount |
|---|---|
| Lender Fees | $500 |
| Closing Costs | $1,000 |
| Other Charges | $300 |
Savings from Lower APR
Choosing a home equity loan with a lower APR can result in significant long-term savings. By minimizing the additional fees and charges included in the APR, borrowers can reduce the overall cost of the loan and save money over time.
Predicting Future Home Equity Loan Rates
Predicting future home equity loan rates involves analyzing various economic indicators and market conditions to forecast potential trends. Factors such as GDP, inflation rates, and interest rates play a crucial role in determining the direction of home equity loan rates. Additionally, housing market conditions, including home prices and inventory levels, can impact the movement of these rates.
Impact of Economic Indicators
- Economic indicators like GDP growth can signal the overall health of the economy, influencing the demand for home equity loans and subsequently affecting interest rates.
- Inflation rates can impact the purchasing power of consumers, leading to changes in borrowing behavior and, consequently, home equity loan rates.
- Fluctuations in interest rates set by central banks can directly impact the cost of borrowing, including home equity loans.
Role of Market Conditions
- Home prices and housing inventory levels can indicate the supply and demand dynamics in the housing market, influencing the availability and terms of home equity loans.
- Changes in Federal Reserve policies, such as adjustments to the federal funds rate, can have a direct impact on interest rates for home equity loans.
- Borrower credit scores and loan-to-value ratios are critical factors in determining the risk profile of borrowers and, consequently, the interest rates offered to them.
Regional Factors and Forecasting
- Local housing market trends and employment rates in specific regions can provide insights into the demand for home equity loans and potential interest rate fluctuations.
- Forecasting future home equity loan rates requires a comprehensive analysis of both national economic indicators and regional factors to capture a holistic view of the market.
Comparison of Prediction Models
- Statistical models: Utilize historical data to identify patterns and trends, offering a quantitative approach to predicting future home equity loan rates. Strengths include data-driven insights, but weaknesses may arise from assumptions made in the model.
- Expert surveys: Gather opinions from industry experts to forecast trends in home equity loan rates. While valuable for qualitative insights, this method may lack empirical evidence for accuracy.
- Econometric models: Combine economic theory with statistical analysis to predict future rates based on a range of variables. Offers a balanced approach but may be complex to interpret for non-specialists.
Forecast for Next 12 Months
Based on historical data analysis, it is projected that home equity loan rates may experience a slight increase over the next 12 months due to rising inflation rates and steady economic growth. This forecast is subject to change based on evolving market conditions and external factors.
Mitigating Risks of Unforeseen Events
While unforeseen events like natural disasters or policy changes can disrupt predicted home equity loan rates, strategies such as diversification of investments, maintaining a strong credit profile, and staying informed about market trends can help mitigate risks associated with external factors influencing loan rate forecasts.
Refinancing Home Equity Loan Rates
Refinancing home equity loan rates involves replacing your current loan with a new one at different terms, usually to secure a lower interest rate or better repayment terms.
Benefits of Refinancing
Refinancing can be beneficial when interest rates have dropped significantly since you initially took out your home equity loan. By refinancing to a lower rate, you can reduce your monthly payments and save money over the life of the loan.
Examples of Cost Savings
For example, if you initially took out a home equity loan at 7% interest and current rates have dropped to 4%, refinancing could save you thousands of dollars in interest payments over time. This can result in lower monthly payments and overall savings on your loan.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, home equity loan rates play a significant role in accessing funds for various financial needs. By staying informed and comparing options, individuals can secure the best rates that align with their goals.