Equity Loan: Understanding, Types, Pros, Cons, And More
Equity loans are a crucial aspect of financial planning, offering individuals a way to leverage their assets for various needs. From understanding the concept to exploring different types and potential risks, this comprehensive guide delves into the world of equity loans with clarity and insight.
Definition of Equity Loan
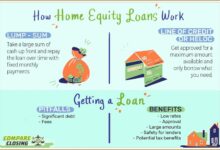
An equity loan, also known as a home equity loan, is a type of loan that allows homeowners to borrow money by using the equity in their homes as collateral. Unlike a traditional mortgage, where the borrower receives a lump sum at the beginning of the loan term, an equity loan provides a line of credit that the borrower can draw from as needed.
Examples of Situations
- Home Improvements: Many homeowners use equity loans to fund renovations or repairs on their property, increasing its value.
- Debt Consolidation: Some individuals use equity loans to pay off high-interest debts, consolidating them into a single, lower-interest loan.
- Education Expenses: Parents may consider taking out an equity loan to cover college tuition costs for their children.
Risks and Benefits
Benefits:
- Lower Interest Rates: Equity loans typically have lower interest rates compared to personal loans or credit cards.
- Tax Deductions: In some cases, the interest paid on an equity loan may be tax-deductible.
Risks:
- Risk of Foreclosure: If the borrower defaults on an equity loan, they could risk losing their home to foreclosure.
- Variable Interest Rates: Some equity loans have variable interest rates, which can lead to higher payments if rates increase.
Obtaining an Equity Loan
- Evaluate Your Equity: Determine the value of your home and calculate how much equity you have available to borrow against.
- Shop Around: Compare offers from different lenders to find the best terms and interest rates for your equity loan.
- Submit an Application: Provide the necessary documentation, such as proof of income and property value, to apply for an equity loan.
- Approval and Disbursement: Once approved, the lender will disburse the funds either as a lump sum or a line of credit for you to access as needed.
Types of Equity Loans
Equity loans come in various forms, each with its own features and benefits. Understanding the differences between these types of loans is crucial in making informed financial decisions.
Home Equity Loans vs. Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs)
Home equity loans provide a lump sum of money upfront, usually with a fixed interest rate and set repayment term. On the other hand, HELOCs function more like a credit card, allowing you to borrow money as needed up to a certain limit and typically have variable interest rates.
Fixed-Rate Equity Loans vs. Variable-Rate Equity Loans
- Fixed-rate equity loans offer stable monthly payments and protection from interest rate increases, suitable for borrowers who prefer predictability.
- Variable-rate equity loans have interest rates that can fluctuate, potentially resulting in lower initial rates but also exposing borrowers to the risk of increased payments in the future.
Cash-Out Refinancing as a Form of Equity Loan
Cash-out refinancing involves replacing your existing mortgage with a new, larger loan and receiving the difference in cash. This can be a way to access your home’s equity and use it for other purposes, but it may increase your overall debt.
Eligibility Criteria for Different Types of Equity Loans
- Home equity loans and HELOCs typically require a minimum amount of equity in your home, a good credit score, and a stable income.
- Cash-out refinancing eligibility is based on factors such as the current value of your home, your existing mortgage balance, and your creditworthiness.
Pros and Cons of Each Type of Equity Loan
| Equity Loan Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Home Equity Loan | Fixed payments, predictable interest rates | Higher interest rates, limited flexibility |
| HELOC | Flexibility to borrow as needed, lower initial costs | Variable rates, potential for higher payments |
| Cash-Out Refinancing | Access to large sums of cash, potential tax benefits | Increased debt, higher closing costs |
Examples of Beneficial Situations for Each Type of Equity Loan
- A home equity loan may be ideal for funding a one-time expense like a home renovation with a fixed budget.
- A HELOC could be advantageous for ongoing expenses such as college tuition where the cost varies each semester.
- Cash-out refinancing might be beneficial for consolidating high-interest debt into a single, lower-rate mortgage.
Potential Risks Associated with Each Type of Equity Loan
High interest rates on a variable-rate equity loan could lead to significantly higher payments over time, potentially straining your finances.
Expert Opinions on Responsible Utilization of Equity Loans
Financial advisors recommend using equity loans for essential investments like home improvements or debt consolidation rather than non-essential expenses to avoid risking your home.
Pros and Cons of Equity Loans
Equity loans can provide homeowners with a valuable financial tool to access funds for various needs. However, like any financial product, they come with both advantages and disadvantages that must be carefully considered before making a decision.
Advantages of Equity Loans
- Low interest rates: Equity loans often come with lower interest rates compared to other types of loans, making them a cost-effective borrowing option.
- Tax-deductible interest: In many cases, the interest paid on an equity loan may be tax-deductible, providing potential savings for homeowners.
- Large loan amounts: Homeowners can typically borrow larger amounts of money with an equity loan, making it suitable for major expenses like home renovations or debt consolidation.
Drawbacks of Equity Loans
- Risk of foreclosure: By using your home as collateral, you risk losing it if you are unable to repay the loan, putting your homeownership at stake.
- Additional fees: Equity loans may come with closing costs, origination fees, and other charges that can add to the overall cost of borrowing.
- Impact on equity: Taking out an equity loan reduces the equity you have in your home, which can limit your options for future borrowing or refinancing.
Improving Financial Situations with Equity Loans
Equity loans can be a strategic tool to improve financial situations by consolidating high-interest debt, funding home improvements that increase property value, or covering unexpected expenses without resorting to high-interest credit cards.
Scenarios where Equity Loans may not be the Best Option
- Unstable income: If your income is unpredictable or you anticipate financial challenges in the future, taking on additional debt through an equity loan may not be advisable.
- Short-term financial needs: For short-term expenses that can be covered by savings or other means, incurring long-term debt through an equity loan may not be the most cost-effective solution.
Uses of Equity Loans
Equity loans offer individuals a versatile financial tool that can be used for various purposes. Let’s explore some common uses of equity loans below.
Home Improvements or Renovations
Using an equity loan to fund home improvements or renovations is a popular choice among homeowners. By tapping into the equity built up in their property, individuals can access a substantial amount of funds to enhance their living space. This can include remodeling kitchens, bathrooms, or adding new additions to the property. The potential increase in property value resulting from these improvements can often outweigh the costs of the equity loan.
Debt Consolidation
Another common use of equity loans is debt consolidation. By consolidating high-interest debts such as credit card balances or personal loans into a single, lower-interest equity loan, individuals can simplify their financial obligations and potentially reduce their overall interest payments. This can help borrowers better manage their debt and work towards becoming debt-free more efficiently.
Investing Options
Individuals may also choose to use funds from an equity loan for investing purposes. Whether it’s investing in a new business venture, the stock market, or other investment opportunities, leveraging the equity in their property can provide individuals with the capital needed to pursue potentially lucrative investment opportunities. However, it’s important to carefully consider the risks involved in investing with borrowed funds and seek professional financial advice before proceeding.
Equity Loan vs. Other Financing Options
When considering financing options, it’s essential to compare equity loans with other alternatives to make an informed decision based on your financial needs and circumstances. Let’s explore how equity loans stack up against different financing options.
Comparison with Personal Loans
Personal loans and equity loans are both popular choices for borrowing money, but they have key differences in terms of interest rates, repayment terms, and eligibility criteria.
- Interest Rates: Personal loans typically have higher interest rates compared to equity loans since they are unsecured, while equity loans use your home as collateral, resulting in lower interest rates.
- Repayment Terms: Personal loans often have shorter repayment terms, usually ranging from 1 to 7 years, whereas equity loans can have longer repayment terms, sometimes up to 30 years.
- Eligibility Criteria: Personal loans rely heavily on credit scores and income for approval, while equity loans consider the equity in your home as a determining factor.
Advantages and Disadvantages compared to Payday Loans
When faced with short-term financing needs, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons of using equity loans versus payday loans.
- Advantages: Equity loans generally offer lower interest rates and more flexible repayment terms compared to payday loans, which often come with extremely high-interest rates and short repayment periods.
- Disadvantages: Equity loans may require more time for approval and involve the risk of losing your home if you default, whereas payday loans can lead to a cycle of debt due to their high costs.
HELOC vs. Personal Line of Credit
For ongoing expenses, understanding the differences between a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) and a personal line of credit is crucial.
- HELOC: HELOCs are secured by your home’s equity, offering lower interest rates and higher credit limits compared to unsecured personal lines of credit.
- Personal Line of Credit: Personal lines of credit are unsecured, meaning they have higher interest rates and lower credit limits than HELOCs.
Risks of Credit Card Cash Advance vs. Equity Loan
When considering financing a large purchase, it’s important to evaluate the risks associated with using a credit card cash advance versus an equity loan.
- Credit Card Cash Advance: Credit card cash advances often come with high fees and interest rates, making them a costly option for large purchases.
- Equity Loan: Equity loans offer lower interest rates and potentially tax-deductible interest, providing a more cost-effective solution for significant expenses.
Cost Comparison with Peer-to-Peer Lending
Comparing equity loans with peer-to-peer lending options can shed light on the total cost of borrowing and any additional fees involved.
- Equity Loans: Equity loans may have lower interest rates and fees compared to peer-to-peer lending, especially for borrowers with strong credit and substantial equity in their homes.
- Peer-to-Peer Lending: Peer-to-peer lending platforms may charge higher interest rates and fees, making equity loans a potentially more affordable financing option in the long run.
Equity Loan Requirements
When applying for an equity loan, there are certain requirements that borrowers need to meet in order to qualify for the loan. These requirements are crucial in determining the borrower’s eligibility and the terms of the loan.
To qualify for an equity loan, borrowers typically need to have a good credit score, a low debt-to-income ratio, and a high loan-to-value ratio. These factors play a significant role in the approval process and the amount of equity that can be borrowed.
Credit Scores and Debt-to-Income Ratios
- A good credit score is essential for qualifying for an equity loan as it demonstrates the borrower’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan.
- A low debt-to-income ratio is also important as it shows that the borrower has sufficient income to cover the loan payments along with existing debts.
Loan-to-Value Ratio Impact
- The loan-to-value ratio determines the maximum amount of equity that can be borrowed. A higher ratio means a lower amount of equity available for borrowing.
- Borrowers with a lower loan-to-value ratio are more likely to qualify for a higher loan amount.
Tips for Improving Eligibility
- Improve your credit score by making timely payments, reducing outstanding debts, and correcting any errors on your credit report.
- Lower your debt-to-income ratio by paying off existing debts and avoiding taking on new debts before applying for an equity loan.
Understanding Credit Scores
Credit scores play a vital role in financial transactions, influencing the interest rates, loan approval, and overall financial health of an individual. Understanding credit scores and how they are calculated is crucial for maintaining a good credit standing.
Factors Influencing Credit Scores
- Payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit used, and new credit applications are key factors that influence credit scores.
Significance of a Good Credit Score
- A good credit score opens doors to better financial opportunities, including lower interest rates, higher credit limits, and easier loan approvals.
Actions to Improve Credit Score
- Make timely payments, keep credit card balances low, avoid opening multiple new accounts, and regularly monitor your credit report for errors.
Late Payments vs. High Credit Utilization
- Late payments can have a significant negative impact on credit scores, while high credit utilization can also lower credit scores.
- It is important to maintain a balance between timely payments and low credit utilization to improve and maintain a good credit score.
Repayment Options for Equity Loans
When it comes to equity loans, understanding the repayment options is crucial for managing your finances effectively. Different repayment structures can have varying implications on the total cost of the loan and your overall financial situation. Let’s delve into the common repayment options for equity loans and how they can impact your financial health.
Interest-Only Payments
Interest-only payments allow borrowers to pay only the interest accrued on the loan for a certain period, typically ranging from 5 to 10 years. During this period, the principal amount remains unchanged. While this option may result in lower monthly payments initially, it can lead to higher costs in the long run as the principal balance is not decreasing. Borrowers need to be prepared for higher payments once the interest-only period ends.
Principal and Interest Payments
Principal and interest payments involve paying both the interest and a portion of the principal balance each month. This repayment structure ensures that the loan balance decreases over time, leading to eventual full repayment of the loan. While monthly payments may be higher compared to interest-only payments, borrowers build equity in their homes and reduce the total cost of the loan over its term.
Implications of Repayment Options
Choosing interest-only payments can result in lower initial payments but higher overall costs due to the extended repayment period. On the other hand, opting for principal and interest payments may lead to higher monthly payments but lower total costs as the loan balance decreases faster. It’s essential to weigh the short-term affordability against the long-term financial impact when selecting a repayment option.
Effective Management Strategies
To manage equity loan repayments effectively, consider creating a budget that includes the loan payments and stick to it diligently. Prioritize making extra payments towards the principal to reduce the overall interest costs and pay off the loan sooner. Monitor your home’s value and equity position regularly to assess your financial situation and explore refinancing options if needed to secure better loan terms.
Risks of Defaulting on Equity Loans
Defaulting on an equity loan can have serious consequences that can impact your financial stability and creditworthiness. It is important to understand the risks involved in order to make informed decisions regarding your loan obligations.
Consequences of Defaulting
- Defaulting on an equity loan can lead to legal actions by the lender, such as foreclosure or asset seizure. This can result in the loss of your home or other valuable assets.
- Defaulting on an equity loan can also have a negative impact on your credit score, making it difficult to secure future loans or credit.
- Lenders may initiate the process of collections to recover the outstanding amount, which can further damage your credit and financial standing.
- In cases of default, lenders may offer negotiation options to settle the debt or come up with a repayment plan. It is important to communicate with your lender to explore possible solutions.
Handling Financial Hardship
- If you are facing financial hardship and struggling to make payments on your equity loan, it is important to seek financial counseling or guidance to explore alternative options.
- Consider refinancing your loan or restructuring your debt to make the payments more manageable and avoid defaulting on your equity loan.
- Communicate with your lender early on if you anticipate difficulties in making payments to discuss potential solutions and avoid the consequences of defaulting.
Tax Implications of Equity Loans
When it comes to equity loans, understanding the tax implications is crucial. Let’s delve into how interest on equity loans can affect your taxes and what you need to know about claiming tax deductions on this type of loan.
Interest Deductibility
Interest on equity loans is often tax-deductible, which can be a significant benefit for borrowers. This means that you may be able to deduct the interest you pay on your equity loan from your taxable income, reducing the amount of tax you owe.
Eligibility for Tax Deductions
To be eligible for tax deductions on equity loan interest, the loan must be secured by your home and the funds must be used to improve the property. If you meet these criteria, you can usually deduct the interest on loans up to $750,000. However, it’s essential to consult with a tax professional to ensure you qualify for these deductions.
Purpose of the Loan
The tax implications of equity loans can vary based on the purpose of the loan. For example, if the funds are used for home improvements, the interest may be fully deductible. On the other hand, if the loan is used for personal expenses or investments, the deductibility of the interest may be limited.
Recent Tax Law Changes
Recent changes in tax laws have impacted the deductibility of interest on equity loans. Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, the deduction for home equity loan interest was limited for certain uses of the funds. It’s essential to stay informed about any changes in tax laws that may affect your ability to deduct interest on equity loans.
Considerations Before Taking Out an Equity Loan
Before deciding to take out an equity loan, it’s essential to carefully consider a few key factors to ensure it aligns with your financial goals and circumstances. Additionally, exploring potential alternatives and thoroughly reviewing your options can help you make an informed decision. Here are some considerations to keep in mind:
Alternatives to Equity Loans
When contemplating taking out an equity loan, it’s crucial to explore alternative options that may better suit your financial needs. This could include personal loans, credit cards, or even borrowing from family and friends. By comparing the advantages and disadvantages of each option, you can determine the best fit for your situation.
Checklist Before Committing to an Equity Loan
– Evaluate your current financial situation
– Understand the terms and conditions of the loan
– Calculate the total cost of borrowing, including interest rates and fees
– Consider the impact on your credit score
– Have a repayment plan in place
Evaluating if an Equity Loan is Right for You
Before proceeding with an equity loan, it’s important to assess whether it aligns with your financial goals and circumstances. Consider factors such as the purpose of the loan, your ability to repay, and the potential risks involved. Consulting with a financial advisor can also provide valuable insights.
Difference Between Home Equity Loan and HELOC
A home equity loan provides a lump sum of money upfront, while a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) allows you to borrow funds as needed, similar to a credit card. Understanding the distinctions between the two can help you choose the option that best suits your needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Equity Loans
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Low interest rates | Risk of losing your home if you default |
| Tax-deductible interest | Potential for increasing debt |
Calculating Risks and Rewards of an Equity Loan
When considering an equity loan, it’s crucial to calculate the potential risks and rewards associated with borrowing against your home’s equity. Assessing the interest rates, repayment terms, and potential appreciation of your home can help you make an informed decision.
Financial Goals Suitable for an Equity Loan
Examples of specific financial goals where an equity loan may be a suitable option include home renovations, debt consolidation, or financing major expenses like education or medical bills. By identifying your financial objectives, you can determine whether an equity loan aligns with your needs.
Equity Loan Regulations and Consumer Protections
Equity loans are subject to various regulations aimed at protecting consumers from predatory lending practices and ensuring fair treatment in the borrowing process.
Regulatory Framework for Equity Loans
The regulatory framework governing equity loans includes laws and regulations that lenders must follow to protect consumers from abusive practices. These regulations set guidelines for transparency, disclosure of terms, and fair treatment throughout the loan process.
Key Laws and Regulations
- The Truth in Lending Act (TILA) requires lenders to disclose key terms and costs associated with the loan, including the annual percentage rate (APR) and total repayment amount.
- The Home Ownership and Equity Protection Act (HOEPA) provides additional protections for high-cost loans, including restrictions on certain fees and terms.
- The Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA) prohibits discrimination in lending based on factors such as race, religion, or marital status.
Consumer Rights and Protections
Consumers have the right to receive clear and accurate information about the terms of their equity loan, including the total costs, repayment schedule, and any potential risks involved. They also have the right to dispute errors on their loan documents and file complaints if they feel their rights have been violated.
Resources for Consumers
There are resources available for consumers to learn more about their rights regarding equity loans, including consumer protection agencies, legal aid organizations, and government websites that provide information on lending laws and regulations.
Fixed-Rate vs. Adjustable-Rate Loans
Fixed-rate equity loans offer stable monthly payments, providing consumers with predictability and protection against interest rate fluctuations. In contrast, adjustable-rate loans may offer lower initial rates but carry the risk of payment increases over time.
Credit Scores and Consumer Protection
Credit scores play a significant role in determining the terms of an equity loan, including interest rates and loan amounts. Consumers with higher credit scores generally receive more favorable terms and better consumer protections compared to those with lower scores.
Filing Complaints and Seeking Recourse
If a consumer believes their rights have been violated in an equity loan agreement, they can file a complaint with the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) or seek legal recourse through private attorneys or consumer advocacy organizations. It is essential to act promptly and gather evidence to support the claim.
Case Studies
Equity loans have been instrumental in helping individuals achieve their financial goals by leveraging the equity in their homes. Let’s explore some real-life examples of how equity loans have been used successfully.
Successful Home Renovation Project
One individual used an equity loan to finance a major home renovation project. By tapping into the equity built up in their home, they were able to access a large sum of money at a lower interest rate compared to other types of loans. This allowed them to transform their outdated home into their dream space, increasing the property value significantly.
Dealing with Unexpected Medical Expenses
Another homeowner faced unexpected medical expenses and turned to an equity loan to cover the costs. Despite the challenges of dealing with the sudden financial burden, the individual was able to secure an equity loan quickly and efficiently. This helped them avoid dipping into their savings or resorting to high-interest credit cards.
Starting a Small Business
An entrepreneur used an equity loan to kickstart their small business venture. With the funds obtained through the equity loan, they were able to cover startup costs, purchase necessary equipment, and establish a solid foundation for their business. The flexibility of the equity loan terms allowed them to manage cash flow effectively during the early stages of the business.
Forecasting Trends in the Equity Loan Market
As we delve into forecasting trends in the equity loan market, it is essential to analyze recent data and market reports to gain insights into the current landscape. By examining historical patterns and economic indicators, we can make informed predictions about how the equity loan market may evolve in the future.
Impact of Interest Rates on Equity Loans
One of the key factors influencing the availability and terms of equity loans is the prevailing interest rates. When interest rates are low, borrowers tend to seek out equity loans as a cost-effective financing option. Conversely, higher interest rates may deter borrowers from taking out equity loans, leading to a decrease in demand.
Housing Market Conditions and Equity Loans
The state of the housing market plays a significant role in shaping the equity loan industry. A booming housing market with rising property values often results in increased equity for homeowners, making them more likely to qualify for larger equity loans. On the other hand, a downturn in the housing market can constrain the availability of equity loans as the collateral value diminishes.
Regulatory Changes and Equity Loan Market Dynamics
Changes in regulations governing the financial industry can have a profound impact on the equity loan market. Stricter lending requirements or new compliance standards may restrict access to equity loans for some borrowers, while promoting greater transparency and consumer protection in the market.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, equity loans serve as a valuable tool for accessing funds based on existing assets. By weighing the pros and cons, understanding the requirements, and considering alternative options, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their financial well-being.